September Research and News 2023
As we delve deep into countless medical journals to uncover the latest on Integrative Medicine's approach to kidney health, we are always reminded of the value of your time. Our commitment remains steadfast in curating and succinctly summarizing these vital studies for you. Welcome to the September Research and News.
Shining New Light: The Epimeric Form of Vitamin D in Kidney Function
A recent study in Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation scrutinizes the role of epimeric form of vitamin D, known as 3-epi-25(OH)D3, in the cardiovascular health of patients with advanced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD).
The research involved 165 patients, including those who had undergone kidney transplantation and those on the waitlist. Patients underwent cardiopulmonary exercise tests and echocardiography at various intervals.
The study found that patients with lower levels of 3-epi-25(OH)D3 showed decreased peak oxygen uptake, which is a crucial marker for cardiovascular capacity.
Moreover, the study revealed that this particular form of vitamin D was linked to cardiovascular functional capacity over time in both transplanted and non-transplanted patients, although it didn't show a significant relationship with other cardiovascular outcomes like left ventricular mass or arterial stiffness.
Understanding the role of 3-epi-25(OH)D3 in cardiovascular health holds significant implications for the treatment and management of advanced CKD patients. Cardiovascular issues are one of the leading complications in CKD, often leading to dire consequences.
The study’s findings present an avenue for potentially modulating cardiovascular function through the management of 3-epi-25(OH)D3 levels.
This could mean more targeted therapies and perhaps a better quality of life for patients struggling with both kidney disease and associated cardiovascular complications.
If you want to learn more about epimeric vitamin D, this review might be helpful.
Unveiling the Link: Metabolic Syndrome, Hyperfiltration, and Kidney Health
This research, published in July 2023, investigates the relationship between metabolic syndrome (MetS), hyperfiltration, and the long-term decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in a non-diabetic general population aged 50 to 63.
Conducted as part of the Renal Iohexol Clearance Survey (RENIS), the study involved 1,551 participants who were free from diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and kidney disease.
The research found that individuals with MetS were more likely to have hyperfiltration at baseline and experienced a faster rate of GFR decline during the 11-year follow-up.
The study quantifies the GFR decline as significantly steeper in individuals with MetS and baseline hyperfiltration compared to those without MetS.
Why is this Important?
This study sheds light on the complex interplay between MetS, hyperfiltration, and long-term kidney function. Given that a quarter of adults worldwide meet the criteria for MetS—a condition known to increase the risk for diabetes and cardiovascular disease—the findings hold broad public health relevance.
Understanding that MetS can lead to hyperfiltration and faster GFR decline offers a new perspective on how metabolic health impacts renal function.
These insights emphasize the need for early interventions in patients with metabolic syndrome to prevent the development of CKD.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic
Mind Over Kidney: The Impact of Psychological Distress on CKD Self-Management
The cross-sectional study, published in August 2023, explores the link between psychological distress and self-management behaviors in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) not on dialysis.
Conducted in four hospitals in The Netherlands, the study used online questionnaires to collect data from 460 CKD patients. The results show that 27.2% of the sample reported experiencing psychological distress, including depressive and anxiety symptoms.
This distress was found to be significantly correlated with poorer dietary adherence, reduced physical activity, and lower medication adherence. However, no significant associations were found with smoking and body mass index.
The study addresses an often-overlooked facet of CKD management: the psychological well-being of patients. The data make it clear that psychological distress is not just a peripheral issue but a significant barrier to effective self-management in CKD.
As the disease already imposes a heavy burden on the healthcare system, understanding the impact of psychological factors can help in the development of targeted behavioral interventions.
Such interventions could be critical for improving adherence to treatment regimens, thereby potentially slowing disease progression and enhancing the quality of life for CKD patients.
The Hidden Risk: Elevated Metal Levels in Exclusive Marijuana Users
The study, published in August 2023, investigates the levels of metals in the blood and urine of exclusive marijuana users.
Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2005–2018), the study included 7,254 participants categorized by their use of marijuana, tobacco, or both.
Five metals were measured in the blood, and 16 were measured in the urine. The results indicated that exclusive marijuana users had significantly higher levels of cadmium and lead in both blood and urine compared to non-users of either substance.
The study reveals a significant public health concern by demonstrating that exclusive marijuana use is associated with elevated levels of toxic metals like cadmium and lead.
Both cadmium and lead have been implicated in the development of kidney disease and hypertension.
As marijuana becomes increasingly legalized and accepted for recreational and medicinal use, the findings emphasize the need for further research on the contaminants found in cannabis.
This can inform regulations and guidelines to ensure the safety of an ever-growing number of cannabis users.
Review Article of the Month
Lipid Dysregulation in CKD: A Pathway to New Frontiers
The review article, published in Nature Reviews Nephrology in July 2023, focuses on the role of lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
The article points out that lipid accumulation in the kidney may drive inflammation and fibrosis, similar to its role in fatty liver diseases.
It discusses the complexity of understanding the link between lipid accumulation and CKD due to the variety of lipid species and their functional roles in different kidney cells.
The review also highlights the potential of newly developed lipid-targeting strategies that can delay or halt kidney disease.
You can download the full PDF here.
Join here to receive FREE monthly updates on the latest research in Integrative Nephrology and tips on managing kidney disease straight to your inbox.
We would love to hear your feedback. Let us know what you think of these educational materials and if you like us to focus on specific topics. Please email us at info@inkidney.com.
Demystifying Oxalate: The Antinutrient Unveiled
When navigating the terrain of nutrition, we often focus on essential nutrients, overlooking the complex world of “antinutrients.” Antinutrients are compounds found in our daily food that might block or reduce our body's ability to absorb essential nutrients. One such critical antinutrient playing a significant role, especially for those concerned with kidney health, is oxalate.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
A Glimpse into the World of Antinutrients
- Phytic Acid: The mineral blocker
- Sources: Grains, seeds, nuts, and legumes are rich in phytic acid.
- Effects: Phytic acid can hinder the absorption of crucial minerals such as iron, zinc, calcium, and magnesium. Phytic acid is helpful in preventing the absorption of plant phosphate. This decreases the phosphate load kidney patients may experience when consuming a plant-dominant diet.
- Management: Techniques such as soaking, sprouting, and fermenting can significantly diminish phytic acid content, rendering the nutrients in these foods more bioavailable.
- Lectins: Gut’s nemeses
- Sources: Legumes like beans and lentils, tomatoes, eggplants, and certain grains are known lectin sources.
- Effects: By binding to the gut wall, lectins can disrupt nutrient absorption.
- Management: Cooking, particularly boiling, can degrade most of the harmful lectins. Pre-soaking beans and legumes also aids in lectin reduction.
- Tannins: The iron obstructor
- Sources: Predominantly found in tea, coffee, and some fruits.
- Effects: Tannins can obstruct non-heme iron absorption, potentially leading to deficiencies.
- Management: Diversifying iron sources and not solely depending on plant-based ones can mitigate the impact of tannins on iron absorption.
- Trypsin Inhibitors: The protein barrier
- Sources: Abundantly present in legumes like soybeans.
- Effects: They can obstruct protein digestion by targeting the enzyme trypsin.
- Management: Comprehensive cooking usually neutralizes these inhibitors.
- Goitrogens: The thyroid disruptors
- Sources: Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower contain goitrogens.
- Effects: These compounds can disrupt thyroid function by inhibiting iodine uptake, vital for thyroid hormone synthesis.
- Management: Regular cooking can substantially neutralize most goitrogenic compounds.
You can see from the above list that many of these “antinutrients” are present in foods that have proven health benefits.
Zooming into oxalate
Oxalate, also known as oxalic acid, is a naturally occurring compound found in many plant-based foods. It's known for its ability to form insoluble crystals when it binds with minerals like calcium and magnesium. These crystals can interfere with mineral absorption. Oxalate can also contribute to the formation of kidney stones in susceptible individuals. For those focusing on integrative approaches to kidney diseases, understanding oxalates is crucial.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic
Oxalate content in common foods:
The oxalate content varies considerably among different foods:
- Very High: Spinach, rhubarb, beet greens, almonds, and Swiss chard contain more than 100 mg of oxalate per serving.
- Moderately High: Foods like okra, sweet potatoes, raspberries, and black tea contain between 50 to 100 mg per serving.
- Moderate: Grapes, celery, green beans, and strawberries contain about 10-50 mg per serving.
- Low: Foods such as melons, bananas, cauliflower, and avocados contain less than 10 mg per serving.
The nutritional conundrum of antinutrients
Antinutrients, including oxalates, can lead to mineral deficiencies such as deficiencies in calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc. For example, long-term excessive intake of oxalate-rich food may decrease the bioavailability of calcium. This can impact bone and dental health if oxalate consumption remains consistently high without a balanced calcium intake.
Oxalates and Kidney Stones
For individuals with a history of kidney stones or those prone to them, oxalates can pose a particular risk. Kidney stones are commonly composed of calcium oxalate. They can be extremely painful and recurrent. They can also lead to kidney failure.
As we discussed in a previous blog, though, a great proportion of the oxalate that is excreted in the urine is actually formed by the liver from the breakdown of animal protein and collagen.
On the other hand, it is important to realize that oxalate content in the food is not as important as its bioavailability (i.e. how much of the ingested oxalate is actually getting absorbed).
A healthy and well-balanced diet containing calcium and magnesium can decrease the amount of absorbed oxalate by binding it in the gut and preventing it from getting absorbed.
Managing Antinutrients Wisely
- Diversifying Diet: A well-diversified diet ensures a variety of nutrients and reduces the risk of excessive oxalate absorption.
- Cooking Methods: Boiling high-oxalate foods can lead to a significant reduction in their oxalate content as a portion of the oxalate leaches into the boiling water. Thus, discarding the water after boiling foods like spinach or beet greens can help.
- Balanced Consumption: Consuming calcium-rich foods alongside high-oxalate foods can be strategic. The oxalate and calcium can bind in the intestines, which reduces the absorption of oxalate and the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Individualized Approach: Not everyone reacts to oxalates in the same way. Factors such as gut health, metabolic differences, and genetics play a role. For those with a history of kidney stones or other related health concerns, a more personalized approach may be needed. Consulting with an Integrative nutritionist or healthcare professional can offer insights tailored to individual health profiles.
The Role of Fiber and Nutrients
While it's crucial to emphasize once again that while is good to be aware of antinutrients, it's equally important to emphasize the positive aspects of plant-based foods. Many of these foods are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals that are essential for overall health. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help counteract the potential negative effects of antinutrients.
The Bottom Line
While oxalate can pose challenges in high amounts, the foods that contain it also offer various health benefits. Understanding the oxalate content in foods and strategizing their consumption can provide the benefits these foods offer without the associated risks. Embrace a holistic and informed approach to nutrition for health-empowered kidneys and life.
The Benefits of Acupuncture in Kidney Disease
Kidney disease, particularly chronic kidney disease (CKD), has become a global health concern, with increasing numbers of patients experiencing complex symptoms. Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, has been gaining attention as a complementary therapy for managing kidney diseases and related complications. This blog explores the benefits of acupuncture in kidney disease, drawing insights from various scientific studies.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
Acupuncture involves inserting fine, metallic needles into the skin, which are then either manually manipulated by the practitioner's precise hand movements or activated through electrical stimulation.
Acupuncture is a component of age-old Traditional Chinese Medicine. Practitioners in this field hold that there are over 2,000 specific points on the human body, interconnected by channels known as meridians. These meridians facilitate a flow of energy, termed Qi ("chee"), vital for overall well-being.
When this energy circulation is disrupted, it can lead to illness. Using acupuncture on designated points is believed to enhance Qi flow, thus promoting better health.
Research has demonstrated that acupuncture can be beneficial for treating multiple conditions. So, let's discuss the role of acupuncture in kidney disease.
The role of acupuncture in kidney disease (CKD)
Enhancing renal function
According to a study conducted by Jung-Sheng Yu et al., on the benefit of acupuncture in kidney disease, acupuncture applied to specific "acupoints" for 12 weeks reduced creatinine levels and increased eGFR levels in CKD patients. These results suggest a potential role for acupuncture in enhancing renal function. This can be due to the effects of acupuncture on improving blood pressure and decreasing inflammation, as we will see below.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic
Improving blood pressure and proteinuria
In a review article on the role of acupuncture in kidney disease, acupuncture was shown to have beneficial effects in controlling hypertension, reducing proteinuria, and correcting anemia in CKD patients. It was thought that acupuncture improved the regulation of the sympathetic system and activated various beneficial bioactive chemicals. These findings indicate the potential for acupuncture to play a role in the overall improvement of renal health.
Acupuncture's effects on symptoms and quality of Life in CKD
Another systematic review of nine studies analyzed the effects of different acupuncture techniques on CKD patients. The studies demonstrated significant benefits in improving quality of life, reducing fatigue, improving depression, and enhancing sleep quality.
Acupuncture techniques have also shown promise in controlling other complications of CKD, such as uremic pruritus (itching).
Anti-inflammatory actions of acupuncture in kidney disease
A comprehensive review addressed the anti-inflammatory actions of acupuncture. This is the most important benefit of acupuncture in kidney disease. Various studies demonstrated the immunosuppressive actions of acupuncture. Furthermore, the potential anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture, mediated through various mechanisms such as neuropeptide release and cytokine balance, may also be beneficial for kidney disease patients.
Another review suggested that the effects of acupuncture may be mediated via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
The Bottom line on the benefit of acupuncture in kidney disease
The application of acupuncture in kidney diseases, especially CKD, offers promising avenues for enhancing renal function, managing symptoms, and improving quality of life. While current evidence demonstrates the potential benefits of acupuncture, more comprehensive and well-designed studies are needed to verify its efficacy and to explore the underlying mechanisms.
Nevertheless, acupuncture's role as a complementary therapy in kidney disease care represents a valuable addition to conventional treatment approaches, potentially offering patients a holistic and integrative approach to managing their condition.
August Research and News 2023
As we delve deep into countless medical journals to uncover the latest on Integrative Medicine's approach to kidney health, we are always reminded of the value of your time. Our commitment remains steadfast in curating and succinctly summarizing these vital studies for you. Welcome to the August Research and News.

Rising incidence of nephrolithiasis: A closer look at the vulnerable group
A study published in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology examined the increasing prevalence of nephrolithiasis (kidney stones) in the United States, focusing on changes in incidence related to age, sex, and race.
The study, based on data from South Carolina between 1997 and 2012, found that the mean annual incidence of nephrolithiasis increased by 1% per year, from 206 to 239 per 100,000 persons.
The study revealed significant demographic shifts in the incidence of nephrolithiasis. The most notable increase was observed among 15-19-year-olds, whose incidence rose 26% per 5 years.
After adjusting for age and race, the incidence increased by 15% per 5 years among females, while it remained stable for males.
Among racial groups, the incidence among blacks increased 15% more per 5 years compared to whites. These changes led to a doubling of the risk of nephrolithiasis during childhood and a 45% increase in the lifetime risk for women over the study period.
Why This is Important?
The study's findings underscore the growing prevalence of nephrolithiasis and reveal shifting risk patterns among various demographic groups.
The significant increase among young patients, particularly women, and among the black population suggests the need for targeted health interventions to manage and prevent this painful condition.
Understanding the drivers of this increase, whether lifestyle-related or otherwise, can guide public health strategies and clinical practices in the coming years.
Link Between vegetable and fruit intake frequency and mortality: Implication for chronic kidney disease patients
In a Japanese hospital-based prospective cohort study published recently, researchers have found a significant link between the frequency of vegetable and fruit intake and mortality rates in both patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and those without the disease.
The study encompassed 2,006 patients and found that lower frequencies of vegetable and fruit intake were associated with a higher risk of death.
This is a particularly important finding as patients with advanced CKD are conventionally often discouraged from consuming high amounts of vegetables and fruits due to the potential risks of hyperkalemia.
However, this study has demonstrated that the frequency of vegetable and fruit intake is indeed associated with lower mortality, regardless of CKD status. The results remained significant even after adjusting for demographic factors, comorbidities, and CKD status.
Why This is Important?
These findings challenge existing dietary recommendations for CKD patients and have significant implications for dietary guidance, potentially prompting a reconsideration of current nutritional advice for CKD patients.
As adequate fruit and vegetable intake is a key part of a balanced and healthy diet, ensuring CKD patients can safely incorporate these food groups may help improve overall health outcomes.
However, this study could be more ideal if it identified the number of servings of fruits and vegetables the participants consumed every day.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic
Dietary vitamin E intake: A protective factor against kidney disease
A cross-sectional study from the NHANES database (2009-2016) involving 20,295 participants examined the relationship between dietary vitamin E intake and the prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in US adults.
The study found a significant negative correlation between high vitamin E intake (8.770 mg/day) and CKD prevalence. This suggests that increased vitamin E intake might be a protective factor against CKD, evidenced by a nonlinear downward trend in the progression to very high-risk CKD as vitamin E intake increases.
The adjusted odds ratio (OR) for high vitamin E intake and CKD prevalence was 0.86, and a similar negative correlation was observed in very high-risk patients, where the OR was 0.51. These associations were found to be stable across populations in a subgroup analysis.
Why This is Important?
This research underscores the potential role of dietary vitamin E in the prevention and progression of CKD. It opens avenues for the exploration of dietary interventions in the management of CKD and raises the need for further investigation to understand the underlying mechanisms.
It also emphasizes the potential benefits of incorporating vitamin E-rich foods into dietary planning and nutritional guidelines for CKD patients. However, it's important to remember that dietary changes should always be discussed with healthcare providers before implementation, especially in patients with chronic diseases.
Elevated uremic retention solutes in CKD: Exploring the role of diet and gut microbiota
This controlled feeding study compared serum and urine concentrations of uremic retention solutes (URS)—indoxyl sulfate (IS), p-cresol sulfate (PCS), and trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO)—and gut microbiota composition in eight adults with moderate chronic kidney disease (CKD) to eight matched adults without CKD.
Results showed that fasting serum URS concentrations were 2.8 to 4.9 times higher in CKD patients compared to controls, indicating a substantial difference in how these metabolic waste products are processed in individuals with CKD.
Interestingly, the study found no significant differences in the composition of the gut microbiota between the two groups. This highlights that while CKD patients had higher levels of uremic retention solutes, it didn't appear to significantly alter their gut microbiota under a controlled diet.
The study also found that the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a measure of kidney function, was inversely related to each serum URS in the whole cohort. This means as kidney function decreased, serum URS levels increased, and vice versa. Within the CKD group, this relationship remained strong for IS and TMAO, but weakened for PCS.
Why This is Important?
This study provides further insights into the intricate relationship between CKD, dietary components, and gut microbiota.
The finding that CKD patients have elevated serum URS concentrations, despite similar gut microbiota compositions as non-CKD individuals, invites more research into how these metabolic waste products are processed differently in CKD patients.
This could lead to the development of dietary guidelines or therapeutic interventions to manage uremic retention solutes, thus improving outcomes in CKD patients.
Future studies are certainly needed to investigate if specific dietary components may differentially alter the microbiota and URS.
New Feature - Review Article of the Month
Novel mechanisms of salt-sensitive hypertension
A concise review in the journal Kidney International highlights recent research on "salt-sensitive hypertension." It emphasizes the roles of the mononuclear phagocytic system in inflammation, the gut-kidney connection, and epigenetic factors.
The review also explores the impact of three specific drug types on salt-sensitive hypertension: sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, and aldosterone synthase inhibitors.
The authors suggest that in addition to kidney-focused mechanisms, it's essential to consider vasoconstrictor processes in comprehending and managing this type of hypertension.
You can download the full PDF here.
Join here to receive FREE monthly updates on the latest research in Integrative Nephrology and tips on managing kidney disease straight to your inbox.
We would love to hear your feedback. Let us know what you think of these educational materials and if you like us to focus on specific topics. Please email us at info@inkidney.com.
The Precautions of Using Various Stomach Medications in Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) alters the body's ability to filter waste and excess fluids, leading to an accumulation of harmful substances. As a result, many CKD patients experience stomach issues, which often necessitate the use of certain medications. However, it's critical to understand the precautions associated with different stomach medications, such as Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs), Histamine-2 Blockers (H2Bs), antacids, Sucralfate, Pepto Bismol and Alka-Seltzer.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
Stomach Medications in CKD
Frequently I am confronted with improper use of various stomach medications in patients with chronic kidney disease. Many of these medications are associated with adverse outcomes in these patients. In this blog, I will discuss most of these medications along with their potential side effects in kidney patients.
Proton Pump Inhibitors - the most commonly used stomach medications
PPIs, like Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, and Lansoprazole, are often used to manage acid reflux and peptic ulcers by decreasing stomach acid production. However, prolonged use may lead to an increased risk of CKD and hasten its progression. PPIs could also induce hypomagnesemia (low blood magnesium level), an exacerbating factor for kidney issues. This blog discussed the full spectrum of PPIs' effects on the kidneys. Using this wean protocol, you can also learn how to safely wean from PPIs.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
Histamine-2 Blockers
H2Bs, such as Ranitidine, Famotidine, and Cimetidine, are generally safer for CKD patients. Still, some can interfere with the kidneys' ability to excrete creatinine through the tubules. This effect is limited to Cimetidine, though. In fact, Cimetidine has been used to accurately measure creatinine clearance (and glomerular filtration rate). Adjusting the dose of these medications in advanced kidney disease is required to avoid toxicity.
Antacids
Antacids, like Tums and Rolaids, are often used as quick relief from heartburn or indigestion. However, some antacids contain aluminum, which can accumulate and lead to toxicity in CKD patients due to their diminished ability to filter these minerals. Such toxicity can result in bone diseases, anemia, cognitive disorders, liver toxicity, and acute kidney injury. Excessive use of calcium-containing antiacids has also been linked to episodes of acute kidney injury.
Sucralfate
Sucralfate, which forms a protective coating over ulcers, contains 21% aluminum by weight. This can accumulate in CKD patients, leading to aluminum toxicity. Furthermore, it can cause constipation and interfere with the absorption of certain medications, like Levothyroxine, commonly prescribed for thyroid issues in CKD patients.
Alka-Seltzer
Alka-Seltzer, used for temporary relief from heartburn and indigestion, contains sodium bicarbonate and aspirin. Each tablet contains 325 mg of Aspirin, 1916 mg of sodium bicarbonate (567 mg of sodium), and 1000 mg of citric acid. Therefore, it is easy to understand that excessive use of Alka-Seltzer can lead to acute kidney injury. Furthermore, high sodium intake from this antiacid can increase blood pressure. Excessive intake can also lead to metabolic alkalosis (increased blood alkalinity), which can cause irregular heart rhythms and death. Therefore, CKD patients should avoid Alka-Seltzer or use it under close medical supervision.
Bismuth
Bismuth is often used for heartburn, acid reflux, “indigestion,” diarrhea, and nausea. The active ingredient is called Bismuth Subsalicylate. The salicylate part of the drug is completely absorbed, while bismuth is not. Bismuth acts in the gut as a bactericidal that also promotes mucosal healing. Each tablet of Pepto-Bismol contains 99 mg of salicylate and 27 mg of calcium. Bismuth compounds have been found to be toxic to the kidneys in a dose-dependent manner. Therefore, bismuth should be used very cautiously in patients with kidney disease.
Natural and Supplement Alternatives
Natural alternatives and supplements can help manage stomach issues without harming kidney health. For example, dietary changes, like eating smaller, more frequent meals, can help manage acid reflux. Supplements like probiotics can improve gut health and reduce gastrointestinal symptoms. Additionally, herbal remedies, such as slippery elm, DGL, chamomile, and marshmallow root, have traditionally been used to soothe stomach issues. However, natural remedies and supplements should be discussed with an Integrative healthcare provider, as some herbs can interact with medications and affect kidney function.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
The Bottom Line
Managing CKD involves carefully considering every medication, given their potential impact on kidney health. While stomach medications can offer relief, their use must be carefully monitored to prevent further kidney damage. Discuss all medication regimens, including natural alternatives, with an Integrative healthcare provider to ensure they're safe and beneficial. Regular monitoring, informed choices, and open communication are key to managing CKD and associated stomach issues effectively.
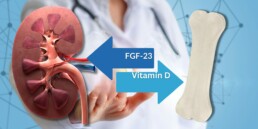
FGF-23 and Kidney Health: A Comprehensive Look at a Complex Relationship
Within the body's intricate symphony, every hormone has a role. FGF-23, or Fibroblast Growth Factor-23, is one such player. Though essential in phosphate regulation, elevated levels of FGF-23 in chronic kidney disease (CKD) have come under scrutiny. Let's explore this multifaceted molecule and understand why it becomes problematic in CKD.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
Understanding FGF-23's Normal Function
FGF-23 is a hormone primarily produced in the bone that helps regulate phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. It maintains phosphate balance, which is essential for building strong bones, cellular function, and energy production. FGF-23 ensures that any excess phosphate gets excreted by the kidneys, thereby preventing a dangerous buildup. But the function of FGF-23 goes beyond merely regulating phosphate.
The Connection Between FGF-23 and Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a significant role in absorbing phosphate from the diet. Its active form, 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D, is crucial for this process. FGF-23 decreases the production of this active vitamin D form, thereby limiting phosphate absorption when needed. In turn, vitamin D can regulate FGF-23 production. This interaction ensures that both phosphate levels and FGF-23 activity are tightly controlled.
The Link Between Phosphate Intake and FGF-23
In today's world, with shifting dietary patterns and increased phosphate intake, especially through processed foods, an overload of this mineral is not uncommon. Even in the early stages of CKD, increased phosphate can push up FGF-23 levels. Managing dietary phosphate is, therefore, a critical part of controlling FGF-23 levels and slowing the progression of CKD.
Challenges in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
In CKD, the kidney's ability to filter phosphate decreases, leading to an increased production of FGF-23. While this response initially helps to maintain phosphate balance, chronically elevated FGF-23 levels become problematic. High FGF-23 levels are associated with further progression of CKD and adverse cardiovascular outcomes.
In addition, the kidneys' reduced ability to convert vitamin D into its active form in CKD means that the FGF-23 and vitamin D regulatory cycle becomes disrupted. This can lead to a dangerous imbalance, making managing the disease even more complex.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
The Klotho Connection: A Key Piece of the Puzzle
Klotho, a protein closely tied to FGF-23, is often called the "anti-aging" protein. In healthy kidneys, klotho assists FGF-23 in its function. However, in CKD, klotho levels decrease, diminishing FGF-23's beneficial effects. This decline, coupled with elevated FGF23, leads to further kidney deterioration and complicates the management of CKD.
FGF-23 in CKD: The Problem with Elevation
While FGF-23's primary role is maintaining phosphate balance, its chronic elevation in CKD is concerning. The kidneys' reduced ability to filter excess phosphate leads to a compensatory rise in FGF-23. Unfortunately, this elevation can spell trouble. High levels of FGF-23 are linked to further progression of CKD and adverse cardiovascular outcomes. What starts as a protective measure turns harmful when chronically elevated.
Phosphate in the Diet: An Overlooked Factor
Increased phosphate intake, often hidden in processed foods, significantly contributes to rising FGF-23 levels. Managing dietary phosphate is vital to controlling FGF-23 levels and slowing down the progression of CKD. Awareness about food sources of phosphate and encouraging phosphate-restricted diets can make a substantial difference in managing CKD.
Navigating the FGF-23-Klotho Axis in CKD
Understanding the dynamics between FGF-23, klotho, and CKD provides insights for better management and treatment options. Innovative therapies targeting the FGF-23-klotho axis are under investigation. Interventions that control FGF-23 elevations or replenish klotho may offer improved outcomes and quality of life for CKD patients.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Identifying and addressing elevated FGF-23 levels in the early stages of CKD might be pivotal in preventing further kidney deterioration. Routine monitoring and early intervention, focusing on dietary management and possible therapeutic options, can significantly impact the course of the disease. Therefore, early restriction of dietary phosphate intake is paramount.
The Bottom Line
The relationship between FGF-23, klotho, and CKD is complex and multifaceted. FGF-23's essential function of maintaining phosphate balance can turn detrimental with chronic elevation, especially when coupled with diminishing klotho. Recognizing these interactions and emphasizing dietary management may be key to improved outcomes for CKD patients. Understanding this delicate balance opens doors to innovative therapeutic strategies that may redefine how we approach kidney health. The continuous exploration of FGF-23's role holds promise for future advancements in CKD treatment and prevention.
Reimagining Public Health: Addressing the Chronic Disease Epidemic
The chronic disease epidemic is one of the most pressing public health challenges of our time. However, I argue that we will not resolve this epidemic using the current system. Understanding the interconnected dynamics of the food industry, pharmaceutical industry, and consumer economy is integral to tackling this problem. The goal is to foster healthier living and better health outcomes for everyone, regardless of their social or economic status.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
The Dichotomy of Wellness
When we take a closer look at who has access to a healthy lifestyle, a significant gap emerges. On one side, there are well-off individuals who have the means to eat healthily and live healthily. They are equipped with the knowledge and resources to maintain a balanced diet and engage in regular exercise. However, the choice to live healthily is an individual one. While some make this choice, others choose otherwise. The point here is not to lay blame but to highlight the fact that they have the freedom to make this choice.
The Struggle of the Disadvantaged
On the other side of the wellness dichotomy, we have the disadvantaged majority. These are the people living paycheck to paycheck, caught in the cyclical nature of financial insecurity and poor health outcomes. For them, it is often not a choice between healthy or unhealthy living. Rather, it's about meeting basic needs within a constrained budget.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
Ultra-Processed Foods: A Cheap But Costly Solution
Consider the affordability of ultra-processed foods. These foods are cheap, readily available, and filling. They are also addictive, leading to overconsumption. For those living on a tight budget, they may appear as a cost-effective solution. However, the long-term health implications of these foods present a different picture. The consumption of ultra-processed foods is linked to various chronic diseases, from diabetes to heart disease. Ultimately, the healthcare costs associated with these conditions far outweigh the initial savings.
The Role of Government and Policies
In this context, the role of government is pivotal. Government policies can greatly influence health outcomes, especially for the disadvantaged. However, the current system often burdens the government with the consequences of poor health policies. Whether it’s paying for the healthcare costs associated with chronic diseases or subsidizing the very industries promoting unhealthy lifestyles, the government finds itself at the center of the chronic disease epidemic. It's clear that a systemic change is needed. Some recommend an excise tax on sugary drinks, tobacco, and alcohol, but this issue is much bigger than that. It goes deep into the fundamentals of the food-pharma-economy complex.
The Allure of Consumerism
Another crucial aspect to consider is the role of the consumer economy. Various industries often target the disadvantaged to purchase the latest gadgets and engage in consumerist behaviors. This cycle of constant buying leaves little room for investment in health, such as buying healthier foods or gym memberships. This is not simply a matter of personal priorities; it's a structural issue that requires systemic solutions.
Beyond Conventional Medicine: A Systems Approach
Addressing the chronic disease epidemic requires a shift away from our traditional medical paradigms. It is not enough to focus on lifestyle medicine, integrative medicine, functional medicine, or even conventional medicine in isolation. What we need is a comprehensive systems approach.
Rethinking the FoodIndustry
As a starting point, we need to transform our food industry. A paradigm shift is required to move away from the current model that prioritizes cheap, ultra-processed foods towards one that values and promotes nutritious, affordable foods.
Pharmaceutical Industry and Health Outcomes
The pharmaceutical industry also plays a key role in this systems approach. Instead of being driven by profit margins, the focus should be on real improvements in health outcomes. This can be achieved by investing in preventative measures and treatments for chronic diseases that are affordable and accessible to all.
Shift in Government Policies
The need for a paradigm shift in government policies cannot be overstated. The current pattern of subsidizing the pharmaceutical and ultra-processed food industries while maintaining a reactive approach towards health in the form of procedural and acute medicine is unsustainable and has yielded less than desirable health outcomes.
Instead, our government must direct efforts and funding toward promoting healthier foods, lifestyles, and preventative measures. This includes policies that incentivize the production and consumption of fresh, nutrient-rich foods, foster environments conducive to physical activity and advocate for healthcare services that prioritize disease prevention.
Such a transformation can create a culture that encourages and rewards healthy choices rather than perpetuating a cycle of chronic illness. While it's true that these changes won't happen overnight, it's a crucial step we must take to stem the tide of the chronic disease epidemic that has taken hold in our society. With the right strategies, we can promote a system where wellness is attainable for all.
The Bottom Line on the Chronic Disease Epidemic
The path to better cost-effective health outcomes is not easy. It requires a complete overhaul of our current systems, from the food industry to the pharmaceutical industry and everything in between. Only then can we truly tackle the chronic disease epidemic and ensure a healthier future for everyone, regardless of their economic or social status.
ما الذي يميز الكلى؟
تحتوي كل كلية على ١-١.٣ مليون نفرون (أو وحدة تصفية كلوية). تكلمت عن وحدات التصفية هذه في هذا الفيديو لمن يرغب بالتذكير. ومن خلال هذه النفرونات تقوم الكلى بتصفية ما يعادل ١٨٠ ليتراً من الدم يوميًا. ورغم ذلك فإن الواحد منا يطرح ١.٥-٢ ليتر من البول يوميًا فقط. فكيف تقوم الكلى بذلك؟ و ما الذي يميز الكلى؟
كما جرت العادة، كل المراجع والمصادر في هذه المدونات ستضاف كروابط ضمن نص المدونة
التصفية بمرحلتين
تحدثنا عن هذا الموضوع سابقاً. وسأذكركم به هنا بشكل سريع لأهميته. تتم عملية التصفية في الكلى على مرحلتين رئيسيتين. تبدأ العملية في الكبب الكلوية، حيث يتم تصفية الدم من الفضلات صغيرة الحجم مع المحافظة على البروتينات والخلايا والجزيئات كبيرة الحجم داخل الدم. في هذه المرحلة تمر العديد من السوائل والأملاح عبر جدار الكبب الكلوية لتشكل مع الفضلات ما يسمى بالرشاحة. وعندما تعلم أن الكبب الكلوية تصفي ما يعادل ال ١٨٠ ليتر يومياً وأن متوسط حجم الدم عند الشخص الطبيعي هو حوالي ال٥ ليترات بإمكانك أن تتفهم أن هذه المرحلة لوحدها لا تكفي
لذلك كان لابد للجسم من استعادة الجزء الأكبر من السوائل والأملاح والشوارد وهذا في المرحلة الثانية أثناء مرور الرشاحة عبر الأنابيب الكلوية. يتم استعادة القسم الأكبر من هذه المواد في الأنابيب الكلوية القريبة في حين تقوم الأجزاء الأخرى من الأنابيب بتعديلات بسيطة نهائية أُشبهها بضبط ألة موسيقية قبل العزف. إن هذه التعديلات البسيطة النهائية على الرشاحة والشوارد والسوائل التي يعاد امتصاصها هو ما يجعل الكلى محورية في ضبط السوائل والأملاح في الجسم
سريرين وعائيين على التوالي
تحتوي النفرونات الكلوية سريرين وعائيين شعريين على التوالي. يدخل الدم إلى الكبب الكلوية من خلال الشُرين الوارد ليشكل أوعية الكبب الكلوية الشعرية ويخرج منها عبر الشُرين الصادر. الدم الصادر من هذه الشُرينات يمر بعدئذٍ من خلال سرير وعائي آخر هو الأوعية الشعرية حول الأنابيب الكلوية
هذه الهيكلية المعقدة تتيح للكلى القدرة على التحكم في ضغط وتدفق الدم في الأجزاء المختلفة من الكلى. إلا أن ذلك يجعل أي مرض يصيب أحد السريرين يؤثر على السرير الآخر. وهذا ما يفسر، على سبيل المثال، سبب حدوث تليف في الأنابيب الكلوية عن حدوث التهابات في الكبب الكلوية
وظائف الكلى المتعددة
تقوم الكلى بوظائف تتجاوز مجرد تصفية الدم من السموم والفضلات. فهي تلعب دورًا هاماً في تنظيم مستوى الماء والصوديوم والبوتاسيوم والكلور والكلسيوم والفوسفات في الجسم. بالإضافة إلى ذلك فهي تساعد في توازن حموضة وقلوية الدم. كما أنها تلعب دورًا في تنظيم ضغط الدم، وتفعيل فيتامين دال، وضبط إنتاج الخلايا الحمراء
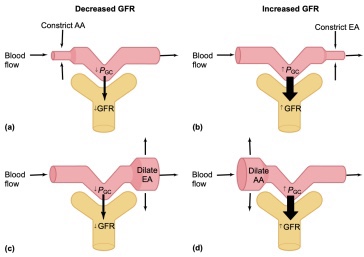
الاعتماد على الضغط داخل الكبيبي
تلعب الشراينات الصادرة والواردة الكبب الكلوية دورًا حاسمًا في تنظيم الضغط داخل الكبب. فالتغيرات في قطر هذه الشرايين يمكن أن تؤثر في كفاءة عملية التصفية. على سبيل المثال، التقلص المفرط للشريين الوارد قد يقلل من تدفق الدم إلى الكبب ويقلل من الضغط داخلها، مما يقلل من كفاءة التصفية ومن معدل الرشح الكبيبي
توسع البروستاغلاندينات الشرين الوارد في حين يقلص الانجيوتنسين ٢ الشرين الصادر. لذلك تؤدي مضادات الالتهاب غير الستيرؤيدية إلى تقلص الشرين الوارد (من خلال تثبيط البروساغلاندينات) بينما تؤدي مثبطات الانزيم القالب للانجيوتنسين إلى توسع الشرين الصادر. هذا ما يجعل استعمال هذه الأدوية معاً مضراً للكلى لأنه قد يؤدي إلى هبوط حاد في الضغط داخل الكبيبات مما قد يؤدي إلى قصور كلوي حاد
الحاجة للكثير من الطاقة
تستهلك الكلى كمية كبيرة من الطاقة للقيام بعملياتها الحيوية. هذه الطاقة تأتي من المتقدرات، الهياكل الخلوية التي تنتج الطاقة. في الواقع، الكلى من أكثر الأعضاء في الجسم حاجةً إلى الطاقة، وهي تستخدم حوالي ٧% من إجمالي نفقات الطاقة اليومية عند الراحة. وهو معدل يعادل ما يستخدمه القلب يومياً
معظم هذه الطاقة تستخدم في عمليات النقل الفعال وإعادة الامتصاص في الأنابيب الكلوية وخصوصاً الأنابيب الكلوية القريبة
انضموا إلى مجموعة طب الكلى المتكامل على الفيسبوك
العرضة للإجهاد التأكسدي
يجعل اعتماد الكلى وحاجتها الكبيرة للطاقة عرضة للإجهاد التأكسدي. فعمليات انتاج الطاقة تنتج أيضاً جذور حرة (كفوق الأوكسيد مثلاً). لدى الجسم والكلى الطبيعيين أجهزة متعددة لإبطال المفعول الضار لهذه الجذور الحرة كجهاز الجلوتاثيون مثلاً
ولكن عندما يتجاوز معدل انتاج هذه الجذور الحرة عن القدرة الطبيعية للجسم على التخلص منها يحدث ما يسمى بالإجهاد التأكسدي. يؤدي الإجهاد التأكسدي إلى أذية في ال دنا وجدران الخلايا مما يسبب تلفاً للخلايا الكلوية ويساهم في تطور أمراض الكلى المزمنة
التحاور مع أعضاء أخرى
أخيرًا، الكلى ليست معزولة عن الأعضاء الأخرى في الجسم. بل تقوم بالتواصل الدائم مع الأعضاء الأخرى مثل القلب والأمعاء والعضلات والدماغ عبر هرمونات ونواقل عصبية تؤثر على وظائف الجسم الأخرى. على سبيل المثال، تنتج الكلى هرمون الرينين، الذي يساهم في تنظيم ضغط الدم
الخلاصة
في الختام، الكلى هي عضو حيوي يلعب العديد من الوظائف الهامة في الجسم. الحفاظ على صحة الكلى يعني الحفاظ على سلامة الجسم كله. عندما نفهم ما يجعل الكلى فريدة، نستطيع العمل بشكل أفضل للحفاظ على صحتها
The Role of Plastic Derivatives in Kidney Damage: An Unseen Risk in Everyday Life
Plastic is everywhere. From food packaging to children’s toys, plastic has become a ubiquitous part of our lives. As we rely more heavily on these synthetic materials, the potential health hazards they pose are becoming increasingly apparent.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
The infiltration of plastic derivatives: Phthalates and BPA
Phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA) are chemical compounds that are added to plastics to enhance their properties. Phthalates are used to make plastics more flexible and resilient, while BPA is used in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. The problem is that these compounds aren't always confined to plastic materials. They can leach out and contaminate the environment, including our food and water. Consequently, we may ingest these plastic derivatives, sometimes daily, without realizing it.
How plastic derivatives impair kidney function
Emerging research suggests a correlation between exposure to plastic derivatives and kidney damage. A study published in the "Science of The Total Environment" revealed that exposure to phthalates may lead to the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The exact mechanism is yet to be fully understood, but it's believed that phthalates induce oxidative stress, triggering an inflammatory response in the kidneys, leading to gradual damage.
Similarly, BPA exposure is associated with negative effects on kidney function. Animal studies have shown that chronic exposure to low doses of BPA can lead to kidney fibrosis, a condition characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix, impairing the kidneys' filtering capability.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
The vulnerable group: Children and plastic derivatives
Unfortunately, children are the most vulnerable to the detrimental effects of plastic derivatives on kidney health. Their developing bodies are more susceptible to the toxic effects of these chemicals. For instance, a study published in "Kidney International" found a significant association between BPA exposure and kidney dysfunction in children. It is, therefore, imperative for us to limit children's exposure to plastic derivatives to protect their long-term kidney health.
Minimizing exposure to plastic derivatives: Strategies for kidney health
Avoiding plastic derivatives entirely can be challenging due to their widespread use. However, there are steps we can take to reduce our exposure:
- Opt for BPA-free and phthalate-free products whenever possible.
- Limit the use of plastic containers for food and drink, particularly when heated, as heat can encourage the leaching of these chemicals.
- Use glass, stainless steel, or other safe materials for food and drink storage.
- Encourage policy changes to regulate the use of these chemicals in consumer goods.
By understanding the connection between plastic derivatives and kidney damage, we can take action to protect ourselves and our loved ones.
The bottom line
While we may appreciate the convenience plastic brings to our lives, we need to be aware of the hidden dangers lurking within. Plastic derivatives such as phthalates and BPA, through their insidious infiltration into our daily lives, pose a risk to kidney health. By raising awareness and making conscious choices, we can mitigate these risks and prioritize the health of our kidneys.
The Dual Nature of Herbs for Kidney Health: Unveiling the Benefits and Risks
When it comes to kidney health, herbs have been employed for centuries due to their medicinal properties. However, it is crucial to recognize that herbs can be a double-edged sword in this regard. While certain herbs can support kidney health, others may pose risks to the kidneys. In this blog post, we will explore the uses of herbs for kidney health, shedding light on their positive and negative impacts. By understanding this delicate balance, we can make informed choices regarding herbal remedies for kidney health.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
Positive effects of herbs for kidney health
Dandelion root: A diuretic and antioxidant boost
Dandelion root, known for its diuretic properties, aids in the elimination of excess fluid from the body. This quality proves particularly advantageous for individuals with kidney disease, as it eases the burden on the kidneys. Furthermore, the dandelion root contains antioxidants, which shield the kidneys from free radicals that can cause damage.
Nettle leaf: Combating inflammation and fluid retention
Stinging nettle leaf, another herb celebrated for its diuretic attributes, reduces inflammation, benefiting individuals with kidney disease. Inflammation can contribute to kidney damage, making nettle leaf an excellent addition to kidney-healthy herbal regimens. Stinging nettle leaves can also be used to prevent kidney stones.
Astragalus: Renal blood flow and proteinuria improvement
Astragalus has been traditionally used in Chinese medicine for kidney health. Studies suggest that it may improve renal blood flow, reduce proteinuria (excess protein in the urine), and potentially benefit individuals with hypertensive kidney disease. However, there is a single report that showed that Astragalus membranaceus can cause increased CA19-9 and liver and kidney cysts.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
Dan Shen: Support for IgA nephropathy and renal fibrosis
Dan Shen, also known as Salvia miltiorrhiza, has shown promise in managing IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). It has been found to decrease renal fibrosis, a common complication of kidney diseases, which can help preserve kidney function.
Cordyceps Militaris: Anti-inflammatory effects and protection from toxic drugs
Cordyceps Militaris, a fungus with potential medicinal properties, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in chronic kidney disease (CKD). It may also provide protection from the toxic effects of certain drugs on the kidneys and has shown promise as an adjunct therapy for managing diabetic kidney disease.
Rehmannia: Support for various kidney conditions
Rehmannia, commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine, has been found to be beneficial for chronic glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, diabetic kidney disease, and inflammation. It exhibits potential in managing these conditions and supporting overall kidney health.
Negative Effects of Herbs on Kidney Health
While the benefits of herbs for kidney health are noteworthy, it is important to acknowledge the potential risks associated with certain herbs. It is advisable to exercise caution when considering the following:
Ephedra: Beware of high doses
While herbs can be beneficial, certain ones can also harm the kidneys. Ephedra, commonly used as a stimulant and weight loss aid, can result in kidney damage, particularly when consumed in high doses or for prolonged periods. It has also been associated with forming kidney stones.
Licorice Root: A cautionary tale of blood pressure regulation
Licorice root contains glycyrrhizin, a compound that can induce pseudohyperaldosteronism. This condition elevates blood pressure and leads to low potassium levels in the blood. It can potentially damage the kidneys, necessitating caution in its usage. There are deglycyrrhizinated licorice products available that don't have these side effects.
Safe Use of Herbs for Kidney Health
While the benefits of herbs for kidney health are promising, it is crucial to consult healthcare professionals before incorporating them into one's routine. These experts can offer personalized guidance regarding the safe usage of herbs and identify potential interactions or risks.
The bottom line
Herbs can play a dual role in kidney health. While some herbs offer support and protection to the kidneys, others can be detrimental. Understanding this delicate balance is vital when considering herbal remedies for kidney health. Consulting healthcare professionals, using herbs in moderation, and incorporating them as part of a comprehensive approach to kidney health are key factors to remember. By doing so, individuals can harness the potential benefits of herbs while safeguarding their precious kidney health.
July Research and News 2023
We combed through multiple medical journals looking for the latest research on the Integrative approach to kidney health. We know your time is valuable, so we curated and summarized these studies for you. Welcome to the InKidney July Research and News.
July Research and New
Sleep Tight, Kidney Right: Unveiling the Link between Extended Sleep, Leg Restlessness, and Chronic Kidney Disease
This study investigated the link between sleep patterns and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) among the Iranian-Kurdish community. The cross-sectional research involved 9,766 participants, with an average age of 47.33 years, and was evenly split between men and women.
The analysis found that CKD was present in 10.83% of the individuals. The time taken to fall asleep and instances of dozing off during the day were both found to be significantly higher in the non-CKD group. In females with CKD, daytime napping and dozing off were more prevalent than in males with CKD.
After adjusting for various factors, a longer sleep duration (> 8 hours/day) was associated with a 28% higher likelihood of CKD compared to a normal sleep duration (7 hours/day). Additionally, participants who reported experiencing leg restlessness had a 32% higher chance of developing CKD.
The study concluded that there might be a link between sleep duration and leg restlessness with CKD, suggesting the regulation of sleep patterns could potentially aid in preventing CKD.
Why is this important?
These findings shed new light on the potential role that sleep regulation could play in CKD prevention and management.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
Unraveling the Genetic Enigma: Genome-Wide Study Sheds Light on Chronic Kidney Disease Progression
This study conducted a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies to understand the genetic aspects influencing the progression of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). The study involved 116,870 individuals with CKD from the Million Veteran Program and Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s DNA biobank.
The analysis primarily focused on the annualized relative slope in outpatient estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), stratified by race/ethnicity and diabetes status.
The study's key findings include identifying the strongest association with the rs77924615 variant near UMOD/PDILT, where each copy of the G allele correlated with a 0.30%/year faster eGFR decline. An association was also observed within BICC1 (rs11592748), where every additional minor allele was linked with a 0.13%/year slower eGFR decline.
In individuals without diabetes, the UMOD/PDILT variant rs36060036 was associated with a 0.27%/year faster eGFR decline per copy of the C allele. In Black participants, faster eGFR decline was associated with variant rs16996674 near APOL1; in Black participants with diabetes, the lead variant rs11624911 near HEATR4 also showed a significantly faster eGFR decline.
Why is this important?
This study is noteworthy as it deepens our understanding of the genetic factors involved in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The information may be instrumental in the development of innovative therapeutic strategies for CKD. Furthermore, the study underlines the importance of personalized medicine, considering the varying genetic factors associated with eGFR decline in patients of different racial/ethnic groups and those with/without diabetes.
However, until testing for these variants is commercially available, these results remain limited to research. It is relevant to mention that Natera's Renasight genetic test can identify genetic variants in UMOD and APOL1 genes.
Unmasking Urine Secrets: New Study Identifies Urinary Metabolites as Indicators of Chronic Kidney Disease Progression
In this study, the research team sought to uncover potential biomarkers for chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression by analyzing the metabolites in urine samples. These samples were collected from 789 CKD patients at the time of kidney biopsy and from 147 healthy subjects.
The study aimed to identify markers signaling a 30% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a doubling of serum creatinine levels, or the onset of end-stage kidney disease.
The researchers identified seven metabolites that showed a clear distinction between healthy individuals and those with stage 1 CKD, as well as a consistent change in pattern from healthy to advanced-stage CKD patients. These metabolites were betaine, choline, glucose, fumarate, and citrate.
These metabolites remained significantly associated with the composite outcome even after adjusting for factors like age, sex, eGFR, the urine protein-creatinine ratio, and diabetes. When these metabolites were added to traditional biomarkers such as eGFR and proteinuria, they significantly enhanced the ability to predict the composite outcome.
Why is this important?
These urinary metabolites not only differentiate healthy individuals from early-stage CKD patients but also exhibit consistent pattern changes in advanced-stage CKD patients. The ability of these metabolites to predict CKD progression significantly improves when combined with traditional biomarkers.
Therefore, these findings could enable early intervention, help monitor disease progression, and potentially guide therapeutic strategies, thereby enhancing the overall management of CKD.
The Power of Ancient Remedies: Chinese Medicine Rehmannia-6 Shows Potential to Stabilize Kidney Function in Diabetic Patients
This study sought to evaluate the real-world effectiveness of Rehmannia-6-based Chinese medicine on the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in patients with type 2 diabetes and severely increased albuminuria. Diabetes is a leading cause of CKD and kidney failure.
In this multi-center trial, 148 adult patients with type 2 diabetes, an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 30-90 ml/min/1.73m2, and a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of 300-5000 mg/g were randomized to either a 48-week add-on protocolized Chinese medicine treatment program (using Rehmannia-6-based formulations) or standard care alone.
The primary outcomes measured were the rate of change in eGFR and UACR between the beginning of the study and the endpoint (48 weeks later). Secondary outcomes included safety and changes in biochemistry, biomarkers, and concomitant drug use.
The results indicated that the estimated rate of change in eGFR was slower in participants treated with the add-on Rehmannia (-2.0 ml/min/1.73m2) compared to those receiving standard care alone (-4.7 ml/min/1.73m2), suggesting a less severe decline with this herb. However, the difference in the rate of change in UACR did not reach statistical significance.
Why is this important?
The study concluded that Rehmannia-6-based Chinese medicine treatment could stabilize eGFR over a 48-week period in patients with type 2 diabetes, stage 2 to 3 chronic kidney disease, and severely increased albuminuria, offering a promising adjunctive therapy.
The Rehmannia-6 preparation contained: Radix-Rehmanniae-Praeparata 15 g/d, Fructus-Corni 7.7 g/d, Rhizoma-Dioscoreae 7.7 g/d, Poria 5.8 g/d, Cortex-Moutan 5.8 g/d, and Rhizoma-Alismatis 5.8 g/d.
Join here to receive FREE monthly updates on the latest research in Integrative Nephrology and tips on managing kidney disease straight to your inbox.
We would love to hear your feedback. Let us know what you think of these educational materials and if you like us to focus on specific topics. Please email us at info@inkidney.com.
الوراثة وصحة الكلى
من المعروف أن المورثات تلعب دوراً هاماً في تحديد العديد من الصفات التي نرثها، بدءًا من لون العينين إلى نوع الشعر ولونه. لكن، هل فكرت يومًا في مدى تأثير المورثات على صحة الكلى؟ في هذه المدونة، سنستكشف معاً عمق الوراثة وكيف يمكن للمتحورات الوراثية أن تؤثر على الكلى ووظائفها. هنا سأتحدث عن الوراثة وصحة الكلى
كما جرت العادة، كل المراجع والمصادر في هذه المدونات ستضاف كروابط ضمن نص المدونة
مبادئ الوراثة
الوراثة هي العملية التي يتم من خلالها نقل الصفات الموروثة من الأبوين إلى الأبناء. تتم هذه العملية من خلال صبغيات تحتوي على المورثات. حيث يرث كلٌ منا ٢٣ صبغياً من كل والد. المورثات الموجودة في هذه الصبغيات، بدورها، تتألف من الحمض النووي الريبي منقوص الأكسجين (دنا)، وهو سلسلة طويلة تحتوي على أربعة حموض نووية: الأدينين ، الثيمين ، السيتوزين ، والغوانين . هذه الحموض النووية تترتب بعدة أشكال فتشكل ما يشبه الشيفرة. تقرأ هذه الشيفرة في ترتيب معين لتكوين البروتينات المختلفة، وهي العناصر الأساسية للوظائف البيولوجية في الجسم. فبإمكانك أن تتخيل أن خلايا الجسم هي مصنع لتكوين البروتينات المختلفة والمورثات هي القالب الذي تستخدمه الخلايا لذلك
المتحورات الوراثية
أي تغيير في الشيفرة الوراثة سيغير من تركيب البروتين المصنوع وقد يؤدي إلى حذفه بالكامل. وهذا ما يؤدي إلى ظهور السمات الشخصية لكلٍ منا. هناك عدة أنواع من المتحورات الوراثية. فهناك متحورات تؤدي إلى إضافة أو حذف حمض نووي معين. وهناك أخرى قد تكون بسيطة، مثل تغيير في حمض نووي واحد و هو ما يسمى بتغيير الشكل بحمض نووي واحد. كما أن هناك متحورات أكثر تعقيداً تؤدي إلى إعادة ترتيب المورثات أو حتى الكروموزومات. تغيير الشكل بحمض نووي واحد هو نوع من المتحورات الوراثية البسيطة يحدث عندما يتم استبدال حمض نووي واحد في تسلسل ال(دنا). يمكن لهذا التغيير أن يغير في وظيفة البروتين الذي ينتج من المورثة ومما يؤدي إلى تغيير في الصفات البيولوجية
الأمراض الكلوية الوراثية
هناك العديد من الأمراض الكلوية التي يمكن أن تُورث، بما في ذلك مرض الكلية المتعددة الكيسات ومتلازمة ألبورت. مرض الكلى المتعدد الكيسات، مثلاً، يحدث عندما يكون هناك تحور في إحدى المورثتين (ب ك د ١) أو (ب ك د ٢) ، مما يؤدي إلى تكوين كيسات في الكلى تضغط على النسيج الكلوي الطبيعي و تؤدي للقصور الكلوي مع مرور الوقت. أما متلازمة ألبورت فهي حالة تنتج عن تحور في المورثات التي تكون الكولاجين من النوع الرابع، وهذا البروتين هو جزء أساسي في بناء جدران الكبب الكلوية وهي مركز تنقية الدم في الكلى. في كلا الحالتين، تؤدي المتحورات الوراثية إلى تطور القصور الكلوي بمرور الوقت
الوراثة وسرعة تطور القصور الكلوي
بالإضافة إلى الأمراض الكلوية الوراثية، تؤثر الوراثة على سرعة تطور القصور الكلوي. فقد أظهرت دراسة حديثة أن هناك عدة مواقع في مورثاتنا ترتبط مع نقص معدل الرشح الكبيبي مع الوقت
جرى هذا البحث على أكثر من مئة ألف شخص يعانون من القصور الكلوي المزمن وأظهرت أن مورثتي ال (يو مود) (أبول ١) ترتبطان بسرعة تطور القصور الكلوي. بالإضافة إلى ذلك أظهر المقال وجود مواقع وراثية أخرى بالقرب من مورثات معينة ترتبط بسرعة تطور القصور الكلوي. بإمكانكم قراءة هذه الدراسة هنا. هذه النتائج تؤكد على العلاقة القوية بين الوراثة وتقدم مرض الكلى المزمن
انضموا إلى مجموعة طب الكلى المتكامل على الفيسبوك
علاقة الوراثة باستقلاب الأغذية
تلعب الوراثة دورا مهما في نوع الطعام الذي يتناوله الشخص. فقد أثبتت الدراسات أن حاسة الذوق عند كل شخص تتعلق بوجود متحورات وراثية معينة. فالأشخاص الذين لديهم فرط في تذوق الطعم المر بسبب وجود متحور وراثي معين يتناولون ٢٠٠ حصة غذائية أقل من الخضروات سنوياً بالمقارنة مع الأشخاص الذين ليس لديهم هذا المتحور
إضافةً إلى ذلك، فإن هضم العديد من الأطعمة يحتاج إلى إنزيمات في الجهاز الهضمي وهذه الانزيمات هي بطبيعتها بروتينات، وأي خلل وراثي في هذه البروتينات يؤدي إلى خلل في العملية الهضمية للنشويات والدسم والبروتينات
بالمقابل استقلاب العديد مما نتاوله يعتمد على مورثاتنا بما في ذلك القهوة والمغذيات المختلفة. فعلى سبيل المثال أثبتت دراسة أن استقلاب الكافيين يختلف من شخص لآخر وهذا ما يسبب اختلاف نتائج الأبحاث حول دور القهوة في تطور المرض الكلوي فهناك أشخاص يستقلبون الكافيين بشكل سريع وأشخاص يستقلبونها بشكل بطيء. إذا شرب الأشخاص بطيئي استقلاب الكافيين أكثر من ثلاثة أكواب من القهوة يومياً يحدث لديهم زيادة تقارب الثلاثة أضعاف في البروتين في البول وسرعة تطور القصور الكلوي المزمن وارتفاع الضغط الدم
علاقة الوراثة باستقلاب أدوية الكلى
الوراثة تلعب أيضًا دورًا في كيفية استجابة الجسم للأدوية. فالمورثات تحدد كيف يمتص الجسم الأدوية، كيف يستقلبها، وكيف يتخلص منها. الاختلافات الوراثية يمكن أن تؤثر على كيفية استجابة الشخص لدواء معين، مثل الأدوية المستخدمة لعلاج أمراض الكلى. أدوية الضغط كاللوسارتان وأدوية زرع الكلى كالتاكروليموس يتأثر استقلابها بوجود بعض المتحورات الوراثية مثلاً. يسمى هذا المجال بـ "الطب الشخصي" أو "الطب الدقيق"، وهو مجال متقدم يهدف إلى توفير العلاج المثالي بناءً على الخاصيات الوراثية للمريض
ما فوق الوراثة
ما فوق الوراثة هو مجال البحث الذي يستكشف التغييرات في تعبير المورثات عن نفسها. فوجود مورثة معينة أو متحور وراثي لا يعني بالضرورة أن تكوّن وتنتج بروتينات. هناك تغيرات كيميائية في ال(دنا) تجعل من بعض المورثات فعالة في حين تجعل أخرى غير فعالة. كل ذلك يعتمد على البيئة التي تعيش فيها الخلايا والرسائل التي تنقل عبر رسل كيميائية من غشائها إلى نواتها. وهذا ما يجعل لنمط الحياة الذي يعيشه كلٌ منا وما نتعرض له من سموم وأدوية ومكملات وما إلى ذلك دوراً مهماً في تعبير المورثات عن نفسها. وهذا أساس التفكير في نهج طب الكلى المتكامل حيث يُقال: إن مورثاتنا لا تملي قدرنا
الخلاصة
فهم الوراثة وكيف يمكن أن تؤثر على صحة الكلى هو مجال بحث مهم ويتطور بسرعة. مع التقدم العلمي والتكنولوجي، أصبحنا نفهم بشكل أفضل كيف تتأثر صحتنا بالوراثة، وكيف يمكننا استخدام هذه المعرفة لتحسين الرعاية الصحية. بفضل الابحاث الحديثة، أصبح بإمكاننا الآن أن نكتشف المتحورات الوراثية التي قد تؤدي إلى أمراض الكلى، وأن نطور استراتيجيات للتعامل مع هذه المشكلات. فبينما لا يمكننا تغيير المورثات التي نُولد بها، يمكننا استخدام هذه المعرفة للسيطرة على المخاطر الصحية التي قد نواجها وتعديل نمط حياتنا بشكل صحي يؤثر إيجابياً على مورثاتنا
Harnessing the Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Kidney Disease Management
Living with a chronic kidney disease diagnosis can be daunting, especially when it comes with a long list of dietary restrictions. Finding a balance between these limitations and ensuring optimal nutrition can be a significant challenge. However, one nutritional approach gaining traction for its potential benefits is the anti-inflammatory diet for kidney disease.
An Overview of the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
The anti-inflammatory diet isn’t a ‘diet’ in the traditional sense - instead, it’s a lifestyle choice that emphasizes the consumption of foods known to combat inflammation and minimizes those that may provoke it. Key components of this diet include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber, they are pivotal in combating inflammation. Variety is key - the more colors on your plate, the broader the nutrient spectrum.
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa. They are rich in fiber and other essential nutrients that can help keep inflammation at bay.
- Lean Protein: Limiting protein intake, in general, is helpful for kidney disease. However, that does not mean that kidney patients should become vegetarians. Choosing lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, and legumes are preferred over red and processed meats.
- Healthy Fats: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish, avocados, nuts, and oils like olive oil, have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Spices and Herbs: Certain spices and herbs, including turmeric, ginger, rosemary, and oregano, have recognized anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Tea and Coffee: These beverages contain antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory effects. However, we recommend that coffee consumption should be based on genetic testing for genetic variations in cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2), which impacts the rate of caffeine clearance. This testing is available through many non-specialized commercially available genetic tests such as ancestry.com and 23andme.com. Slow metabolizers of caffeine should avoid drinking more than 3 cups of coffee daily.
- Conversely, it’s recommended to limit or avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, red and processed meats, and trans fats.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Kidney Disease: A Potential Game-Changer
Chronic kidney disease often goes hand-in-hand with elevated inflammation levels. This inflammation can accelerate the progression of the disease and contribute to other complications, such as cardiovascular disease. The anti-inflammatory diet for kidney disease may help manage these symptoms by reducing inflammation, potentially slowing disease progression.
However, kidney disease patients often need to navigate specific dietary restrictions related to their condition, such as limiting potassium, phosphorus, and sodium intake. Therefore, it’s vital to collaborate with an Integrative or Functional medicine healthcare provider or a renal dietitian when planning to incorporate this diet into your lifestyle. Tailoring the diet according to each patient’s needs and type of kidney disease is crucial for success.
The bottom line
The anti-inflammatory diet, when implemented correctly, could prove to be a powerful tool in managing kidney disease. Always remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes. They can provide tailored advice based on your unique nutritional needs and health status. As the saying goes, ‘Let food be thy medicine,’ and let this diet be a step towards better kidney health.
Boost Kidney Health with Glutathione: Exploring Selenium, Oxidative Stress, and Ferroptosis
Understanding the role of glutathione, the master antioxidant, is key to ensuring kidney health. One of the leading lines of defense in our body against oxidative stress and ferroptosis, glutathione plays a pivotal role in keeping our kidneys in optimal health. This blog post will delve into the connection between selenium and glutathione, the damaging effects of oxidative stress and ferroptosis on kidney health, and how we can support our body’s glutathione levels, including the use of liposomal glutathione.
Selenium: A Key Player in Glutathione Levels
The trace mineral selenium is an integral part of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which is central to our body’s antioxidant defense mechanism. GPx combats oxidative damage by neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS are highly reactive, unstable molecules our bodies produce during normal metabolism and in response to environmental stresses. They can cause damage to cells if they aren't properly controlled by our natural antioxidant systems. Keeping a balanced selenium intake is essential to maintain healthy glutathione levels, which is crucial for robust kidney health. To read more about the role of selenium in protecting the kidneys from oxidative stress, read this blog.
How Oxidative Stress Affects Your Kidneys
When ROS production surpasses your body’s capacity to neutralize them, oxidative stress occurs. This condition leads to inflammation, cellular damage, and, in extreme cases, cell death. Kidneys are especially prone to oxidative stress due to their high energy needs and robust blood supply. Over time, oxidative stress can cause kidney damage, and worsen existing conditions, leading to fibrosis (scarring). This will lead to faster progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
Ferroptosis: An Emerging Concern for Kidney Health
Ferroptosis is a newly identified form of regulated cell death distinguished by iron accumulation which leads to increased ROS. ROS then interacts with lipids in the cell membranes causing cellular death. It has significant implications for various health conditions, including kidney damage. Glutathione aids in preventing ferroptosis by neutralizing ROS and sustaining the function of the GPx4 enzyme, thereby protecting cells from lipid peroxidation. You can read more about it here.
Bolstering Glutathione Levels for Optimal Kidney Health
You can see now that supporting glutathione is crucial for better kidney health. Here are some ways to boost the body’s glutathione levels:
- Selenium supplementation: Ensuring proper selenium intake can support glutathione levels and fortify kidney health. Brazil nuts, fish, and whole grains are excellent dietary sources of selenium. Patients with kidney disease should aim for 200 mcg of selenium daily, either through high-quality supplements or diet. This can be easily accomplished by eating only two Brazil nuts a day.
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC): NAC is a glutathione precursor that can enhance its levels in the body. Studies suggest that NAC supplementation can positively affect kidney function in CKD patients. There isn't a standard dose for NAC, but clinical studies for various conditions have used doses ranging from 600 to 1800 milligrams per day, typically divided into 2 or 3 doses. We use Pure Encapsulation NAC 600 mg capsules at a dose of 1200 mg twice a day. However, it's essential to start with a lower dose to assess tolerance and consult an Integrative or Functional medicine-certified provider.
- Liposomal glutathione: Liposomal glutathione, a form of glutathione encapsulated in liposomes for improved absorption, may be more effective in boosting glutathione levels than other forms, according to some studies. This study showed that doses of 500-1000 mg were sufficient to reduce markers of oxidative stress. However, it's best to follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult an Integrative or Functional medicine healthcare provider
- Antioxidant-rich diet: Food is medicine. Consuming a diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide various antioxidants that support glutathione levels and overall kidney health.
The bottom line
Boosting glutathione levels is key to maintaining kidney health. Understanding the roles of selenium, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis allows us to take active steps in protecting our kidneys. By supplementing with selenium, NAC, or liposomal glutathione and adopting a diet rich in antioxidants, we can ensure optimal glutathione levels for overall kidney health.
طب الكلى المتكامل: نهج شخصي لرعاية الكلى
يجمع الطب التكاملي أو المتكامل بين ممارسات وعلاجات الطب البديل مع ممارسات الطب التقليدي. بإمكانك تصوره كجسر بين الطب الوظيفي وطب الأسلوب الحياتي والطب التقليدي. يركز الطب المتكامل على العديد من الأمور التي تتراوح بين التغذية و التمارين الرياضية و أسلوب الحياة الصحي والصحة العقلية. فهذه العوامل تساهم معاً في تسبيب الأمراض المزمنة مثل مرض الكلى. في هذه المقالة، سأناقش ما هو طب الكلى المتكامل وكيف يمكن أن يحدث فرقاً في حياة المرضى المصابين بأمراض الكلى
مفهوم طب الكلى المتكامل
يركز طب الكلى المتكامل على ستة مجالات أساسية تحدد عوامل الخطر الفردية لمرض الكلى لتطوير خطة تعديل نمط الحياة الشخصية التي يمكن دمجها في المقاربة التقليدية للمرضى. هذه المجالات تغطي التغذية، النشاط البدني، التدخين، استهلاك الكحول، والتعرض للسموم البيئية وصحة الأمعاء والصحة الذهنية. وهذا قد يؤدي إلى تحسين حالة المرضى وتحسين النتائج الصحية على المدى الطويل. وتشمل هذه المجالات ما يلي
الوراثة وما فوق الوراثة فمن غير الممكن معرفة خصوصية الشخص بدون معرفة مورثاته التي قد تؤثر على ظهور أمراض معينة وعلى سرعة استقلاب الشخص للأدوية والكافيين مثلاً وما إلى ذلك. أما فوق الوراثة فهو علم يتعامل مع تأثير البيئة بمختلف أشكالها على تعبير المورثات عن نفسها بإظهار الأمراض أو تقليلها
أسلوب الحياة الشخصي بما في ذلك النوم والنشاط البدني والتدخين وطريقة التعامل مع التوتر النفسي فقد أثبتت العديد من الدراسات أن هذه العوامل تؤثر على صحة الكلى
التغذية ورغم أنها واحدة من أساليب الحياة إلا أننا خصصنا لها بنداً خاصاً لأهميتها ولعلاقة ما يدخل الجسد عن طريق الطعام بظهور أمراض متعددة أو الوقاية منها
محور الأمعاء والكلى فتحتوي الأمعاء على الملايين من الباكتيريا بأعداد ومورثات تفوق نظيرتها الموجودة في جسم. وتفرز هذه الباكتيريا مواد متعددة يمتص جسم الإنسان وهناك حوار متواصل بين هذه البكتريا وخلايا الجسم. بالإضافة إلى ذلك فإن سلامة جدار الأمعاء مهم جداً في الوقاية من العديد من الأمراض المزمنة. وفي حالة أمراض الكلى المزمنة تكتسب صحة الأمعاء أهمية خاصة سأتحدث عنها لاحقاً
التعرض للسموم البيئية التي تلوث كل ما حولنا بما في ذلك الماء الذي نشربه والطعام الذي نأكله والهواء الذي نستنشقه والمفروشات التي نجلس عليها وغيرها من الملوثات التي نتعرض لها يومياً وتؤثر على صحة الكلى بشكل مباشر أو غير مباشر
الأدوية، فلا شيء في طب الكلى المتكامل يمنع من استعمال الأدوية وعليك الهرب من أي ممارس يدعي أنه سيشفي الكلى بدون إلى الأدوية، ولكن بالمقابل لا ينبغي أن تستخدم الأدوية كبديل عن ممارسة نمط حياة صحي
انضموا إلى مجموعة طب الكلى المتكامل على الفيسبوك
أهمية طب الكلى المتكامل
يؤثر القصور الكلوي المزمن على الملايين في العالم كما رأينا سابقاً وغالباً ما يرتبط بالعديد من الأمراض المصاحبة مثل أمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية والسكري وارتفاع ضغط الدم. ويمكن أن يؤدي استخدام الطب المتكامل إلى تحسين علاج هذه الأمراض والمساعدة في تقليل تأثيراتها السلبية على الكلى. يقدم طب الكلى المتكامل الأدوات والاستراتيجيات اللازمة لمساعدة المرضى في تحسين صحة الكلى
النهج المتكامل لرعاية مرضى الكلى
يهدف طب الكلى المتكامل إلى تحديد السبب الجذري لمرض الكلى وتحديد العديد من العوامل التي تساهم في سرعة تطوره. و يركز بشكل رئيسي على المبادئ الستة الأساسية التي ذكرت أعلاه لتحديد عوامل الخطر الفردية لمرض الكلى لتطوير خطة تعديل نمط حياة شخصية يمكن دمجها في رعاية المريض بخاصيته و يتم ذلك من خلال ثلاثة مراحل
التوعية
يتطلب تغيير التركيز من النهج الطبي التقليدي نحو النهج الطبي المتكامل لاستثمار الوقت والجهد في توعية المرضى وحول هذا المرض الصامت والقاتل وضرورة التداخل الباكر لإيقاف تطوره ولمنع المضاعفات. وهناك حاجة لتثقيف المرضى حول أنماط الحياة البديلة التي قد تختلف حسب نوع المرض الكلوي وخاصية المريض
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، من الضروري تثقيف مختلف الممارسين حول مبادئ طب الكلى المتكامل والأدوات المستعملة للتقييم وأنواع تحاليل مستعملة لم يعتادوا عليها سابقاً لتحديد خاصية المريض
إضفاء الطابع الشخصي
تتطلب مقاربة الطب المتكامل لأمراض الكلى فريقًا متكاملاً من أطباء الكلى المدربين على مبادئ وأساليب وأدوات الطب المتكامل مع أخصائيي تغذية مدربين و مرشدين صحيين. يقوم هذا الفريق بتقييم وتحليل جميع العوامل المرتبطة بالمبادئ الستة لتصميم "خطة تعديل نمط حياة خاصة بهذا المريض" يمكن دمجها مع مقاربة الطب التقليدي له
الإرشاد
وبالرغم من كلما سبق، لا يكفي وصف خطة تعديل نمط الحياة للمريض فقط. فقد أثبتت الدراسات أن الواحد منا يحتاج وسطياً ل ٦٦ يوماً للالتزام بعادة جديدة. حتى أن البعض يحتاج إلى فترة أطول من ستة أشهر لتأسيس عادة جديدة. لذلك، يحتاج المرضى إلى مرشدين يساعدوهم على تنفيذ الخطة الحياتية الشخصية التي وصفت لهم بما في ذلك من التسوق لشراء البقالة اللازمة، و التدريب على إعداد الوجبات، والتعامل مع التوتر النفسي وحتى العلاقات مع الآخرين، وتحسين النوم، وما إلى ذلك
يمكن سد هذه الفجوة من قبل مرشدين تم تدريبهم على نهج طب الكلى المتكامل ويعملون تحت إشراف أخصائيي الكلى وأخصائيي التغذية. قد يكون هذا المرشد مساعدًا طبيًا مدربًا بشكل كافٍ. فقد أثبتت الدراسات أن المرشدون من أمثال هؤلاء قد يساعدون في تحسين ضبط الداء السكري والتحكم في الكوليسترول. وقد تم استخدام المرشدين الصحيين في المملكة المتحدة لهذا الغرض. وهذا جزءٌ مهمٌ جداً لنجاح نهج طب الكلى المتكامل
الخلاصة
طب الكلى المتكامل يعتمد على نهجٍ مبتكر وشامل لرعاية أمراض الكلى. ويلعب دورًا هاماً في توعية المرضى و من ثم إيجاد خطة خاصة بكل منهم لتغيير نمط حياتهم وارشادهم على هذه الخطة بما يضمن صحة الكلى. وبفضل هذه المقاربة التي تعتمد على المبادئ الستة التي ذكرت أعلاه يمكن تحسين جودة حياة المرضى برأيي والقضاء على وباء القصور الكلوي المزمن
Redefining Kidney Care in the USA: Unleashing the Power of an Integrative Kidney Care for a Global Impact
Within the sprawling landscape of the American healthcare system, a critical issue clamors for immediate action: our deeply flawed approach to kidney care. At the crossroads of a financial catastrophe and traditional medical dogmas, a beacon of hope emerges— integrative kidney care. This groundbreaking approach can potentially spark a radical transformation not just domestically but on a global scale.
By Majd Isreb, MD, FACP, FASN, IFMCP
Unmasking the Financial Behemoth: The Unsustainable Burden of Kidney Care
Presently, the USA wrestles with a formidable financial behemoth: a jaw-dropping $37 billion spent annually on dialysis-related care for End-Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD) (USRDS, 2022). This does not include the additional $75 billion spent by Medicare in 2020 on fee-for-service for advanced CKD patients. This figure isn’t just another statistic; it’s a stark reflection of a system heavily biased toward late-stage interventions. In contrast, early Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) detection and management lurk in the shadows, underfunded and underestimated, escalating healthcare costs exponentially.
The Overlooked Frontier: The Gap in Early CKD Detection and Care
But this isn’t merely a financial battle; it’s also a clinical one. The key casualty? Early CKD detection and care. As a case in point, in 2020, only 9% of the 35 million CKD patients in the USA were aware of their condition (CDC, 2023).
In fact, even in patients with advanced CKD, only 1/3 are aware of their kidney disease. This glaring gap has allowed CKD to stealthily progress to ESKD, boosting reliance on expensive dialysis treatments and overshadowing the importance of preventive care.
This is confirmed by a report published in the Lancet in 2020 about the global burden of kidney disease. The report found a great gap in the early detection of CKD worldwide, even in high-income countries.
The Elephant in the Room: Shortcomings in Conventional Medical Research
Adding to this troublesome state of affairs is the conventional medical research model. Often critiqued for its narrow focus, traditional research primarily champions drug development and late-stage, neglecting early detection and preventive strategies. Despite CKD affecting an estimated 11-13% of the global population, preventive research remains woefully inadequate (Hill et al., 2016).
Conventional medical research is mostly funded by pharmaceutical companies with massive research budgets. This allows these companies to sponsor large-scale clinical trials led by medical university professors and get them published in prestigious medical journals. Subsequently, they use these researchers as speakers to promote their products at various medical conferences and meetings.
Pulling Back the Curtain: Professional Practice Guidelines and the Pharmaceutical Influence
Professional practice guidelines, heavily influenced by pharmaceutical sponsorship, compound the problem. These guidelines are frequently sculpted by expert opinions, which may harbor biases due to pharmaceutical interests. The unfortunate outcome is that less profitable but potentially impactful approaches, like lifestyle and nutritional changes, are marginalized.
A study published by JAMA Network found a significant interaction between clinical practice guideline authors and the pharmaceutical industry. That was in 2002. Now, the process is more sophisticated. The pharmaceutical companies not only pay "grants' to the researchers of large clinical trials, but they also pay them as consultants to promote their products and publish Letters to the Editors to raise awareness about the need for the new approach. Subsequently, lobby to include the products in clinical practice guidelines using the same consultants and lobby insurance companies to pay for them.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
Echoing Beyond Borders: The Impact of US Research on the Global Approach to Kidney Care
The American approach to kidney care sends ripples far beyond its shores. As a leading powerhouse in healthcare research, the USA’s research priorities significantly mold global health policies and practices. A landmark shift in American research could, therefore, spearhead a worldwide revolution in kidney care. The US is not only exporting medical research to the world, but it is also exporting the Western lifestyle with its poor diet, lifestyle habits, and stressors. This explains the rising obesity rate in the world.
Breaking New Ground: The Integrative Kidney Care
This necessitates a rewrite of the narrative—an Integrative approach to kidney care. A perfect illustration of this progressive strategy is the landmark DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) study. It concluded that diet, particularly low sodium and high fruit and vegetable intake, significantly lowered blood pressure, a key risk factor for CKD (Sacks, et al., 2001). There are many other studies that link the Mediterranean diet with improved kidney outcomes. Similarly, research has begun to explore the role of the microbiome, dental health, and environmental toxin exposure management in kidney health, thus painting a holistic picture of kidney care.
However, in order for these lifestyle interventions to make an impact, they have to be implemented at earlier stages of CKD. This is what makes early detection a key.
The Promise of Change: Financial and Health Benefits of Integrative Kidney Care
The integrative approach promises more than just improved health outcomes—it also heralds substantial savings. Investment in targeted early detection could yield a net benefit of $10.2 billion, according to this report from Australia. By integrating early intervention with comprehensive care, annual savings could be much more, showcasing the far-reaching economic potential of this strategy.
The Bottom Line
The cry for a significant pivot in kidney care in the USA from a late-stage focus to integrative kidney care is both a health imperative and an economic necessity. Embracing this shift could redefine patient outcomes, cut healthcare expenditures, and pave the way for innovative global kidney health practices. The urgency for this change is not just critical—it's palpable for the betterment of our nation and, indeed, the world.
القصور الكلوي المزمن: وباء عالمي يتطلب مقاربة جديدة
يصيب القصور الكلوي المزمن ملايين الناس في جميع أنحاء العالم، وغالبًا ما يرتبط بأمراض أخرى مثل السكري وارتفاع ضغط الدم و أمراض المناعة الذاتية. تشير الإحصاءات إلى أن هذا المرض بلغ مرحلة تعادل الوباء، حيث يعاني حوالي ١٥% من السكان في الولايات المتحدة منه. حيث أظهرت البيانات أن هذا الداء قد أصاب أكثر من ٤٥ مليون شخص في الولايات المتحدة وأكثر من ثلاثة ملايين في كندا
الإحصاءات العالمية تختلف من دولة إلى أخرى حسب تطور الطب الوقائي و القدرات في البلدان المختلفة. و لكن أظهرت دراسة نشرت في مجلة اللانسيت عام ٢٠٢٠ أن ما يقارب من ١٠٪ من سكان العالم مصاب بالقصور الكلوي المزمن. بمعنى آخر واحد من كل عشر قرُاء لهذه المدونة لديه قصور كلوي مزمن
القصور الكلوي المزمن مرض الصامت
يعتبر الداء السكري و ارتفاع ضغط الدم السببان الرئيسان للقصور الكلوي المزمن. معاً، يشكلان ٧٠٪ من أسباب القصور الكلوي في العالم. و يتطور القصور الكلوي المزمن ببطء غالبًا وبدون أعراض واضحة، مما يجعله "مرضًا صامتًا". و قد تمر عدة سنوات قبل أن يكتشف مرضى القصور الكلوي أنهم مصابون به. و للأسف عند ظهور الأعراض يقارب المريض من الحاجة إلى التحال الكلوي
يصيب القصور الكلوي المزمن النساء أكثر قليلًا من الرجال و لكن تطوره أسرع عند الرجال لأسباب مختلفة سأذكرها في مدونة قادمة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك يلعب العرق و الحالة الاقتصادية-الاجتماعية دورًا في حدوث و تطور القصور الكلوي
و يصنف القصور الكلوي لخمسة مراحل كما ذكرت في مدونة سابقة. و تعتبر المرحلة الثالثة هي الأكثر شيوعًا
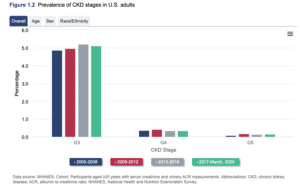
عوامل خطر الإصابة بالقصور الكلوي المزمن
تشمل عوامل خطر الإصابة بالقصور الكلوي: الداء السكري ، وارتفاع ضغط الدم ، وأمراض القلب ، والسمنة ، و وجود قصة عائلية للفشل الكلوي ، والتقدم بالعمر لما فوق الستين و الحصيات الكلوية المتكررة
يعاني العديد من مرضى القصور الكلوي من أمراض خفية في القلب و الأوعية. و عندما تم ترتيب أسباب الوفيات في الولايات المتحدة تبين أن القصور الكلوي المزمن هو تاسع سبب للوفاة. بمعنى آخر، يقتل القصور الكلوي المزمن عدداً من الناس أكثر من سرطان الثدي و من سرطان البروستات. بالرغم من هذه الأرقام المذهلة ، إلا أنك لا ترى أي حملات وطنية أو عالمية فعالة للتوعية بأمراض الكلى. و لذلك فإن نشر التوعية عن أمراض الكلى و القصور الكلوي هو أحد أهم أهدافي من هذه المدونات
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، هناك ثغرات عالمية في مقاربة مرضى القصور الكلوي: ثغرات في الكشف المبكر و المعالجة المبكرة، ثغرات في العلاج بشكل عام و ثغرات في توفر التحال الكلوي و الزرع
التكلفة السنوية
لا توجد احصائيات عالمية موثوق بها حول كلفة علاج القصور الكلوي. إلا أن هذه الدراسة أظهرت أن تكلفة علاج القصور الكلوي أعلى من تكلفة علاج أمراض القلب و الأوعية في العديد من البلدان. و في الولايات المتحدة، أظهرت البيانات الوطنية أن تكلفة علاج مرض القصور الكلوي في ٢٠٢٠ قد بلغت ٨٥.٤ بليون دولار أو ما يقارب من ربع النفقات الصحية لمؤسسة الميديكير الوطنية
الحاجة لمقاربة جديدة
الطب التكاملي أو المتكامل، الذي يجمع بين الطرق التقليدية والعلاجات البديلة والتكميلية، يقدم مقاربة جديدة لمعالجة هذا الوباء العالمي. يسعى الطب المتكامل و الوظيفي إلى الوصول إلى السبب الجذري للداء الكلوي لتحسين جودة حياة المرضى، وليس فقط تخفيف الأعراض و معالجة النتائج. تسأل هذه المقاربة لماذا أصيب هذا الشخص بالداء السكري أو ارتفاع ضغط الدم أو القصور الكلوي وليس فقط كيف يعالج ذلك. تبحث عن خاصية الشخص و ظروفه الحياتية و الغذائية التي قد تؤدي لظهور هذه الأمراض لمقاربتها من ناحية جذرية. تولي هذه المقاربة اهتمامًا أكبر للعوامل الوراثية والتعرض للعوامل البيئية و لتغيير النمط الحياتي والنظام الغذائي للشخص
الخلاصة
أصبح القصور الكلوي المزمن بمثابة وباء عالمي واسع الانتشار. هناك حاجة ماسة للتوعية بأمراض الكلى و القصور الكلوي المزمن، كما أن هناك حاجة ملحة لتحسين الوقاية والكشف المبكر عن هذه الأمراض. يتطلب ذلك برأيي مقاربة جديدة للوقاية والعلاج. الطب المتكامل، مع تركيزه على الشخص ككل، قد يكون الطريقة الأمثل لمعالجة هذا الوباء
June Research and News 2023
We combed through multiple medical journals looking for the latest research on the Integrative approach to kidney health. We know your time is valuable, so we curated and summarized these studies for you. Welcome to the InKidney June Research and News.
June Research and News
DHA-Containing Diets May Halt the Progression of Kidney Disease
A new study in the journal Kidney360 offers compelling insights into the role of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)-containing diets in attenuating renal failure.
The research team sought to examine the effects of arachidonic acid (ARA) and/or DHA on oxidative stress and fibrosis — two key factors that cause kidney injury in rats that underwent a 5/6 nephrectomy. The procedure, which involves the removal of a significant part of the kidney, often leads to increased urinary albumin excretion and eventual renal failure.
Sprague Dawley rats were divided into groups and fed either ARA, DHA, or both for four weeks post-nephrectomy. Researchers assessed urine, plasma, and kidney samples for signs of oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis.
Findings revealed that nephrectomy induced a surge in urinary albumin excretion, indoxyl sulfate, reactive oxygen species, tumor necrosis factor-α levels, and kidney fibrosis. However, these factors were notably reduced when the rats were fed a DHA-containing diet.
DHA-containing diets could be a promising strategy to suppress the progression of kidney disease.
Join us to end the kidney disease epidemic and receive the FREE Report “5 Pitfalls to Avoid When Caring for Kidney Patients”
No Increased Risk of First-Time Symptomatic Kidney Stones from Outpatient Antibiotic Use
A recent population-based case-control study suggests that outpatient antibiotic use does not lead to an increased risk of a first-time symptomatic kidney stone episode. This conclusion runs contrary to the theory that antibiotics, which modify gastrointestinal and urinary microbiomes, could contribute to kidney stone formation.
The study, conducted in Olmsted County, Minnesota, from 2008-2013, involved 1,247 individuals with chart-validated, first-time symptomatic kidney stones, along with 4,024 age- and sex-matched controls.
Researchers analyzed all prescriptions for outpatient oral antibiotics used within the five years preceding the onset of symptomatic stones for both cases and their matched controls.
The findings revealed that the risk of symptomatic kidney stones only increased during the year following antibiotic use. This risk was less after adjusting for comorbidities. Moreover, upon excluding cases and controls with prior urinary symptoms (which could warrant antibiotic prescriptions due to undiagnosed kidney stones), no increased risk of symptomatic kidney stones was noted during the year after antibiotic use.
These outcomes remained consistent across different antibiotic classes and the number of antibiotic courses taken.
Accordingly, the study suggests that the perceived risk of first-time symptomatic kidney stones associated with antibiotics may be largely attributable to the presence of comorbidities and the prescription of antibiotics for urinary symptoms that may actually signal undiagnosed kidney stones, suggesting a case of reverse causality.
Of course, this study, as it is titled, does not address asymptomatic kidney stones or recurrent kidney stones. It also just appears that the researchers cherry-picked their exclusion criteria to get to the negative association.
Lower Incidence of Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome during Covid-19 Pandemic Lockdown - Viral Triggers?
This study is a hidden gem.
Here, researchers examined the incidence of "idiopathic" nephrotic syndrome (INS) during the Covid-19 pandemic, focusing on cohorts in the Netherlands and the Paris area from 2018-2021.
The findings indicated no significant difference in INS incidence before and during the pandemic. However, there was a lower incidence observed during periods when schools were closed.
Notably, during peak times of hospital admissions due to Covid-19, no new INS cases were reported.
The researchers concluded that: the lower incidence of INS, other respiratory viral infections, and reduced air pollution during lockdown suggest a potential link between INS onset and viral infections and/or environmental factors.
Very Low-Carbohydrate Diet Shows Greater Health Improvements Than DASH Diet for High-Risk Adults
A recent randomized trial compared the effects of a very low-carbohydrate (VLC) diet to the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet for adults with hypertension, prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, and overweight or obesity.
The study is relatively small. It included 94 adults from southeast Michigan and found that, compared to the DASH diet, the VLC diet resulted in greater improvements in systolic blood pressure, glycated hemoglobin (an indicator of blood sugar control), and weight loss over a four-month period.
Adding extra support strategies, such as mindful eating, positive emotion regulation, social support, and cooking, didn't significantly affect the outcomes.
This suggests that the VLC diet might offer more effective disease management for this high-risk group than the DASH diet. We look forward to larger, longer-term studies in the near future to confirm these findings.
Join here to receive FREE monthly updates on the latest research in Integrative Nephrology and tips on managing kidney disease straight to your inbox.
We would love to hear your feedback. Let us know what you think of these educational materials and if you like us to focus on specific topics. Please email us at info@inkidney.com.